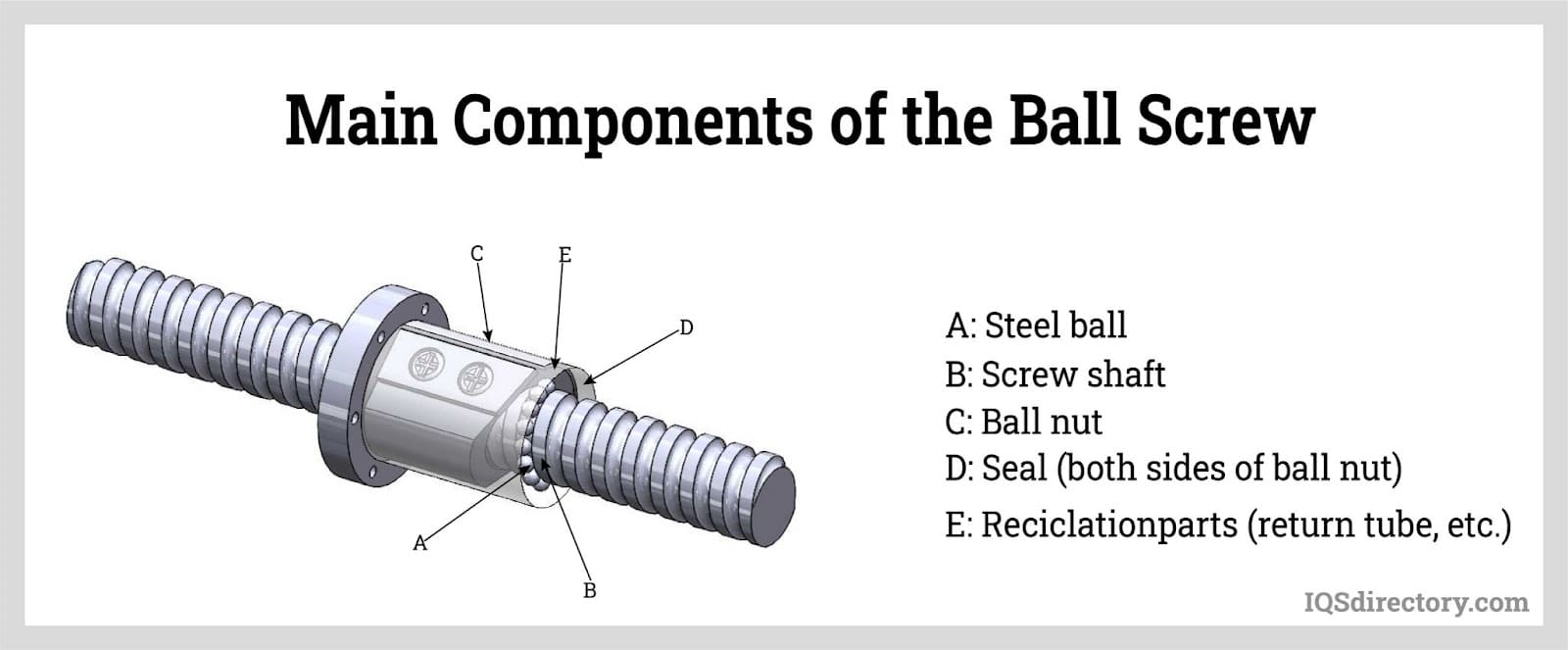
Because ball bearings are made up of small spheres, they have a small point of contact with the load. Therefore, ball bearings come in handy when loading small objects. However, as the stresses increase, these bearings tend to shatter or lose their defined shape. A ball bearing is a rolling-element bearing used to promote motion by carrying weights, reducing friction, and positioning moving machine elements. Surface contact and friction across moving planes can be reduced using ball bearings to separate two “races,” or bearing rings. Read More…
With a multitude of bearing and slide designs available, both standard and custom designed models, Del-Tron Precision Inc. is proud to be a one-stop shopping experience for customers with linear motion needs.
TUSK Direct is a company that produces high quality linear motion components such as linear bearings as well as assemblies for automated equipment.
Isotech is a distributor of precision linear motion components -- crossed roller linear bearings, ball slide assemblies, crossed roller slide tables, motorized tables, position stages and more.
At Hartford Technologies, we take pride in our commitment to precision engineering and cutting-edge technology, positioning ourselves as a leading provider of linear bearings. With a rich history rooted in excellence, we have consistently pushed the boundaries of what's possible, delivering high-performance linear bearings that cater to diverse industrial needs.

More Linear Ball Bearing Manufacturers
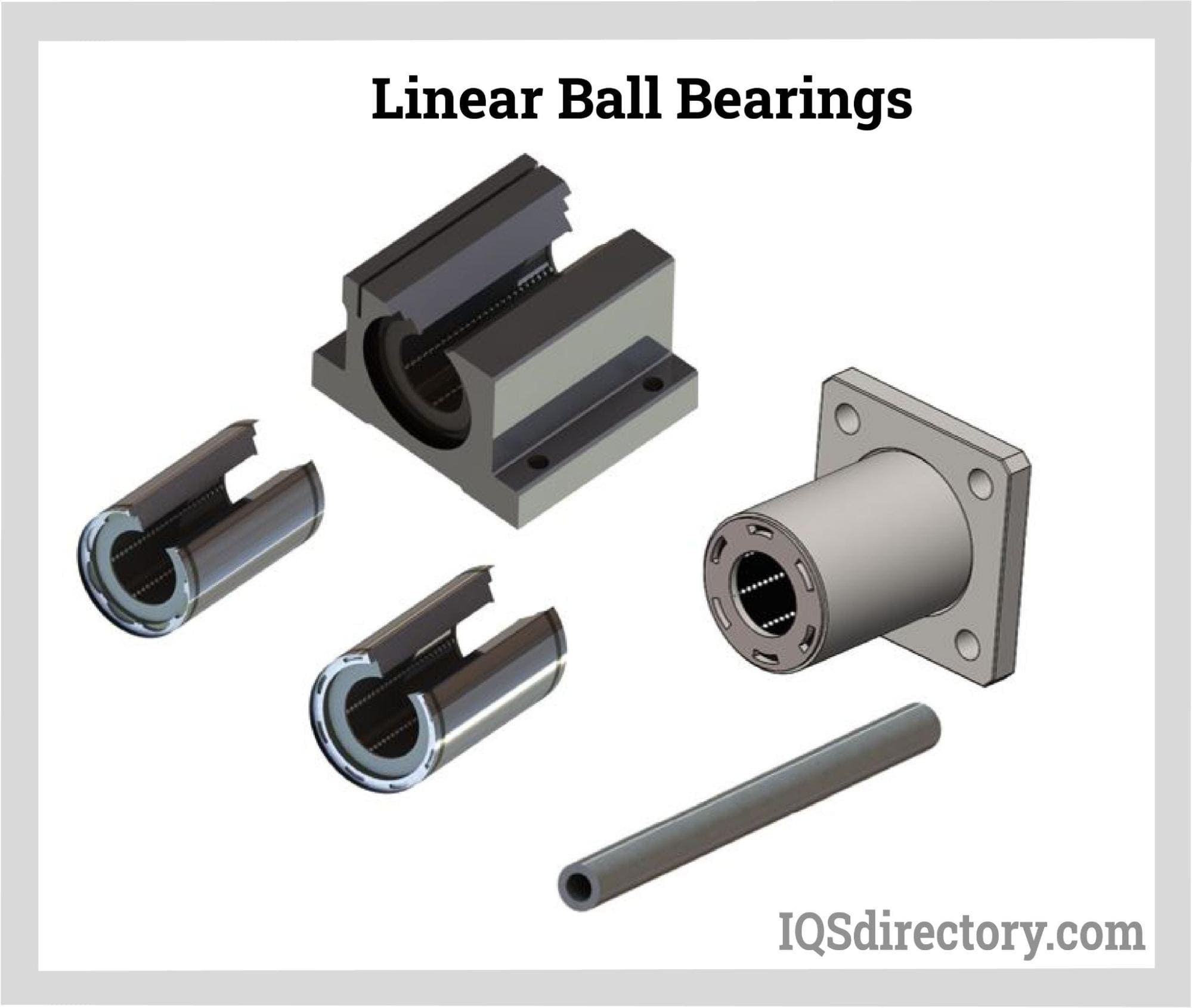
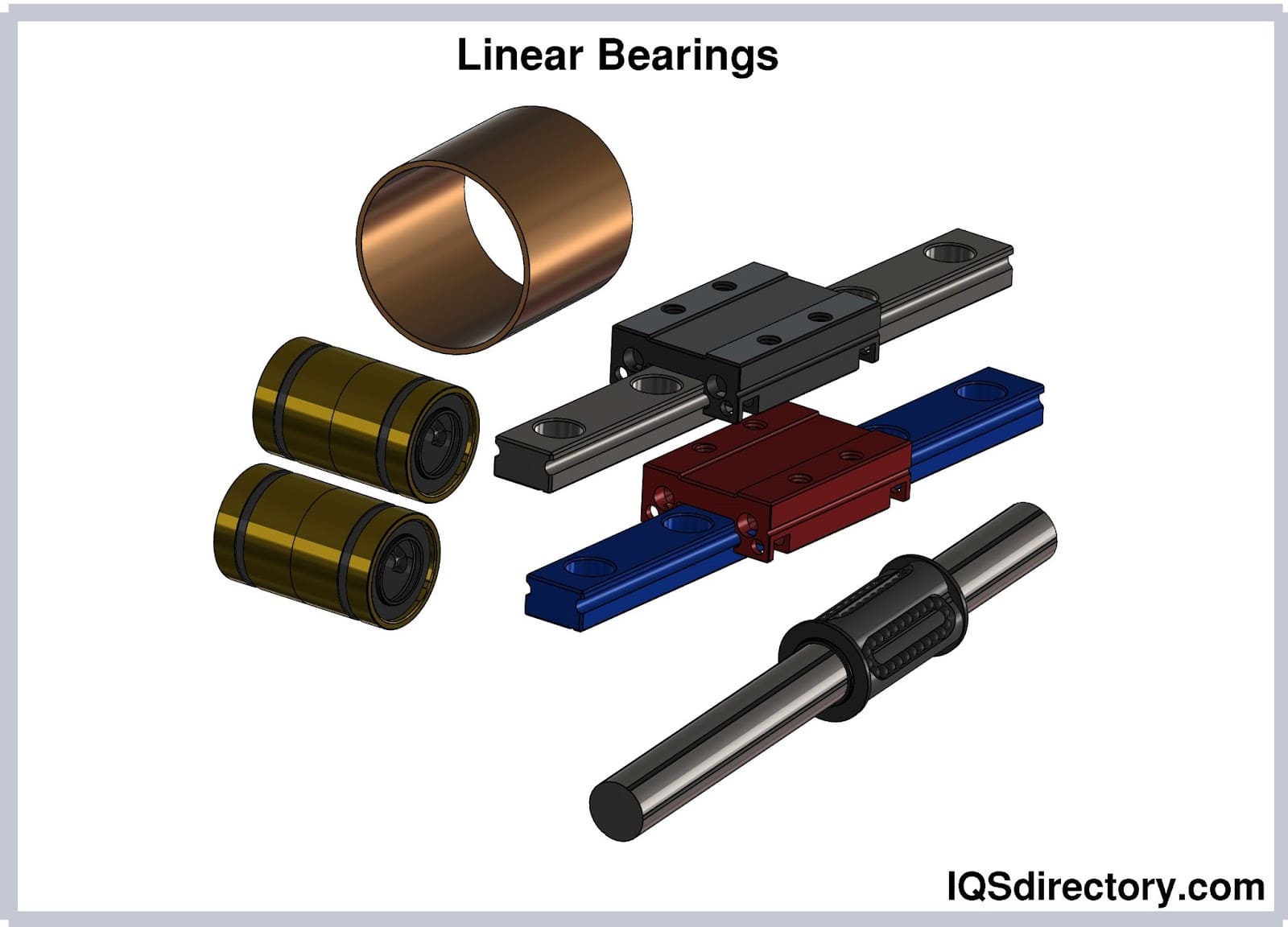
Types of Ball Bearings
- Angular Contact Ball Bearings: When it comes to bearings, angular contact balls have a certain contact angle that distinguishes them from other types. As a result, forces are transferred from one raceway to the next at an angle to the first. Loads requiring strong axial forces and those transferred by the radial motion of ball bearings can also be moved. High radial-axial loads and high speeds are possible with angular contact ball bearings. They are asymmetrical for manufacturing and can only withstand unidirectional axial loads. Angular bearings are typically installed in groups of two or more opposed preloaded units separated by rigid or elastic spacers.

- Self-Aligning Ball Bearings: The inner ring and the ball complement can rotate within the outer ring. Because of an outer ring racetrack that circles the outer ring continually, the options for self-aligning ball bearings are nearly endless in size and design. The inner ring of a self-aligning bearing has two raceways, while the outer ring consists of a single round raceway with its center of curvature coincident with the bearing axis. The two raceways of the self-aligning ball bearings allow the inner ring, balls, and cage axis to automatically correct misalignment caused by machining or installation error of the housing and shaft by deflecting around the bearing center.

- Thrust Ball Bearings: Thrust ball bearings are typically made up of two bearing disks, each with a raceway for the balls in between the ball bearings. It can absorb axial loads in only one direction and orient the shaft in only one direction. Thrust ball bearings are designed to withstand axial (thrust) loads at high speeds but not radial. Bearing washers having raceway grooves in which the balls moved are used in these bearings. Thrust ball bearings are divided into two varieties based on the shape of the housing washer (outer ring seat) and whether they are single-direction or double-direction. Seat washers that are spherical and aligned aid in providing tolerance for installation faults.

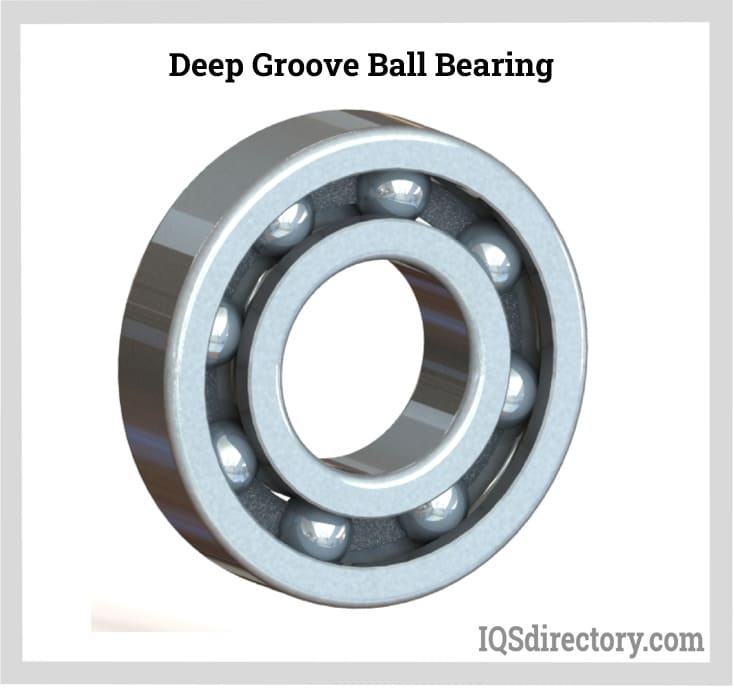
- Deep Groove Ball Bearings: In this form of bearing, a ring of balls is trapped between the two races that allow rotational motion. These balls have exceptionally low friction when held in place by a retainer. This bearing is intended for reduced vibration and noise, making it perfect for high-speed applications. Because of their versatility and overall performance, roller bearings are the world's most widely used type of bearing. They are distinguished by deep raceway grooves in which the inner and outer rings have circular arcs with a slightly larger radius than the balls. They also have rings that cannot be separated.

How Ball Bearings Work
Ball bearings are the most often used type of bearing in rotary movement applications, accounting for more than half of all such applications. They consist of a row or rows of balls wedged between the inner and outer raceways. In most cases, one ring is connected to the rotating assembly or shaft, and the balls roll around the inner raceway when the assembly rotates. On the other hand, the other ring remains stationary, as shown in the above figures. It allows for rotational movement with an extremely low friction coefficient, making it excellent for applications requiring high speeds while still demanding low-friction features.
Applications of Ball Bearings
- In machine-tool ways
- In sliding doors
- 3D printers
- Household equipment
- Automotive
- Office equipment
- Industrial
Advantages of Ball Bearings
- Have a high wear resistance
- Less lubrication is required.
- Ability to withstand thrust loads
- They can be replaced easily.
- Can offer lengthy service
- Linear ball bearings are easy to maintain.
Limitations of Ball Bearings
- They can get quite noisy at times.
- They are incapable of handling heavy loads.
- Shocks may cause damage.
- Linear ball bearings are highly-priced.
Conclusion
Linear ball bearings aid straight-line motion by reducing friction. The choice of which type of ball bearing to use depends on the system for which it is to be applied. Ball bearings are wear-resistant, which means they can be used for a long time with little lubrication. However, they cannot handle heavy loads and are sensitive to shocks.
Choosing the Right Linear Ball Bearing Manufacturer
To make sure you have the most productive outcome when purchasing a linear ball bearing from a linear ball-bearing manufacturer, it is important to compare at least four manufacturers using our list of linear ball-bearing manufacturers. Each linear ball bearing manufacturer has a business profile page that highlights their areas of experience and capabilities and a contact form to directly communicate with the manufacturer for more information or requests a quote. Review each linear ball bearing company website using our patented website previewer to get an idea of what each business specializes in, and then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple linear ball bearings companies with the same quote.








 Air Cylinders
Air Cylinders Assembly Machinery
Assembly Machinery Ball Bearings
Ball Bearings Electric Motors
Electric Motors Fractional Horsepower Motors
Fractional Horsepower Motors Friction Materials
Friction Materials Linear Actuators
Linear Actuators Linear Bearings
Linear Bearings Linear Slides
Linear Slides Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services